What is a Risk Register?
Our safety specialists discuss
A Risk Register is an essential Risk Management Process tool. Representing the identified current recorded and assessed risks present in an organisation, it is a step-by-step guide to the close-out process. Ultimately, the risk register presents the Accountable Manager with a window into the immediate safety and quality status of the company.
Litson and Associates’ safety specialists have created a sample risk register flow diagram which consists of three phases, to demonstrate the easy implementation of this useful tool
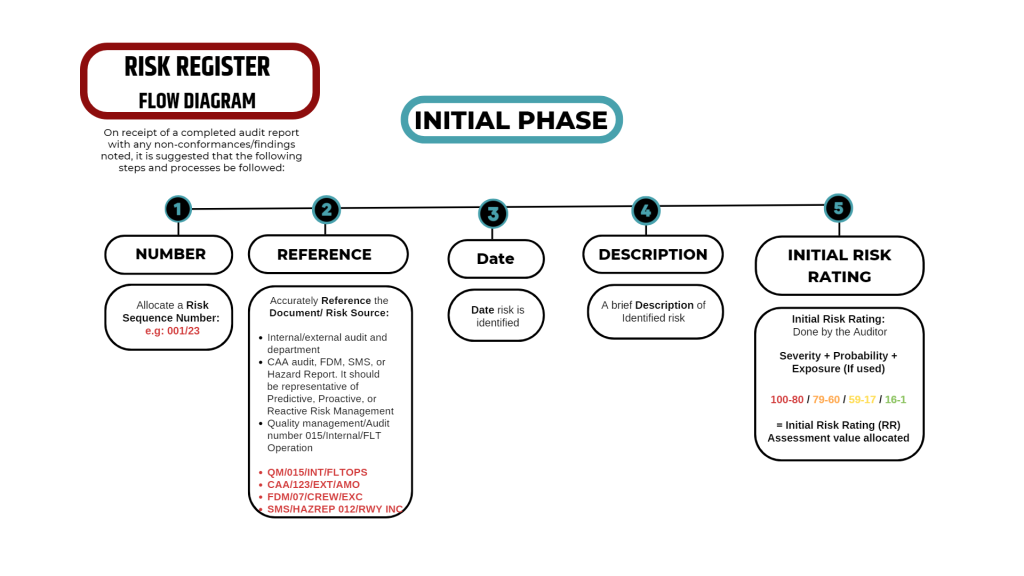
RISK REGISTER FLOW DIAGRAM
On receipt of a completed audit report with any non-conformance/findings noted, it is suggested that the following steps and processes be followed:
- NUMBER
- Allocate a Risk Sequence Number: eg: 001/123
- REFERENCE
Accurately Reference the Document/Risk Source:
- Internal/external audit and department
- CAA audit, FDM, SMS, or Hazard Report. It should be representative of Predictive, Proactive or Reactive Risk Management
- Quality management/Audit number 015/Internal/FLT Operations
- QM/015/INT/FLTOPS
- CAA/123/EXT/AMO
- FDM/007/CREW/ EXCEEDANCE
- SMS/HAZREP 012/RWY INCUR
- DATE
- Date risk is identified
- DESCRIPTION
- A brief description of Identified risk
- INITIAL RISK RATING
- Initial Risk Rating: Done by the auditor
- Severity + Probability + Exposure (if used)
- 100-80 / 79-60 / 59-17 / 16-1
= Initial Risk Rating (RR) Assessment value allocated
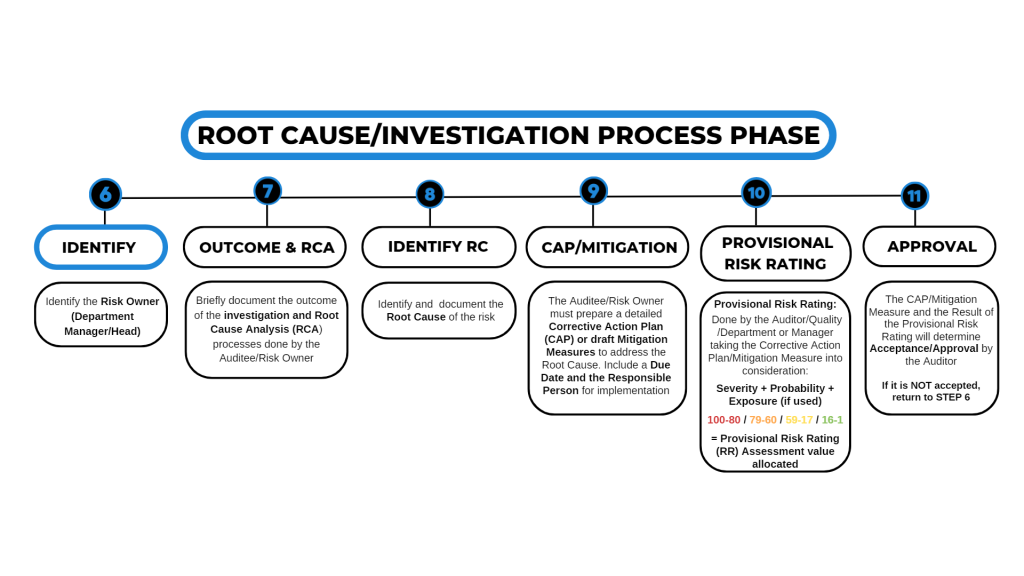
6. IDENTIFY
-
- Identify the Risk Owner (Department Manager/Head)
7. OUTCOME & RCA
-
- Briefly document the outcome of the investigation and Root Cause Analysis (RCA) processes done by the Auditee/Risk Owner
8. IDENTIFY RC
-
- Identify and document the Root Cause of the risk
9. CAP/MITIGATION
-
- The Auditee/Risk Owner must prepare a detailed Corrective Action Plan (CAP) or draft Mitigation Measures to address the Root Cause. Include a Due Date and the Responsible Person for implementation
10. PROVISIONAL RISK RATING
-
- Provisional Risk Rating: Done by the Auditor/Quality Department/Manager taking the Corrective Action Plan/Mitigation Measure into consideration:
- Severity + Probability + Exposure (if used)
- 100-80 / 79-60 / 59-17 / 16-1
= Provisional Risk Rating (RR) Assessment value allocated
11. APPROVAL
-
-
The CAP/Mitigation Measure and the Result of the Provisional Risk Rating will determine Acceptance/Approval by the Auditor
-
If it is NOT accepted, return to STEP 6
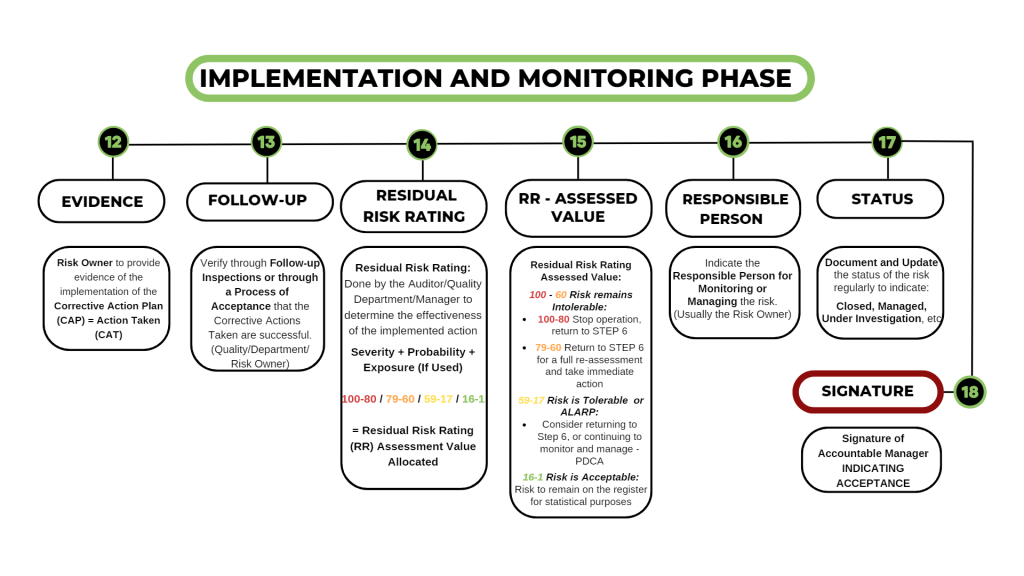
12. EVIDENCE
- Risk Owner to provide evidence of the implementation of the Corrective Action Plan (CAP) = Action Taken (CAT)
13. FOLLOW-UP
Verify through Follow-up Inspections or through a Process of Acceptance that the Corrective Actions Taken are successful (Quality/Department/
Risk Owner)
14. RESIDUAL RISK RATING
Residual Risk Rating: Done by the Auditor/Quality Department/Manager to determine the effectiveness of the implemented action
- Severity + Probability + Exposure (If Used)
- 100-80 / 79-60 / 59-17 / 16-1
= Residual Risk Rating (RR) Assessment Value Allocated
15. RR – ASSESSED VALUE
Residual Risk Rating Assessed Value:
100 – 60 Risk remains Intolerable:
- 100-80 Stop operation, return to STEP 6
- 79-60 Return to STEP 6 for a full re-assessment and take immediate action
59-17 Risk is Tolerable or ALARP:
- Consider returning to Step 6, or continuing to monitor and manage – PDCA
16-1 Risk is Acceptable:
- Risk to remain on the register for statistical purposes
16. RESPONSIBLE PERSON
- Indicate the Responsible Person for Monitoring or Managing the risk. (Usually the Risk Owner)
17. STATUS
Document and Update the status of the risk regularly to indicate:
- Closed, Managed, Under Investigation, etc
18. SIGNATURE
- Signature OF Accountable Manager INDICATING ACCEPTANCE